What is an IP address?
The acronym IP stands for the term Internet Protocol. Internet protocol is a set of rules used to communicate between devices or domains that are connected to the internet or a network. An IP address is a unique number assigned to a specific device or a domain name. This number is an identifier. In other words, the IP address is the coordinates to your device or domain and ensures that the correct data is routed to and from the correct device or domain.
At the present, we have two versions of IP addresses, IPv4 and IPv6. Because future demand for IP addresses will exceed the capabilities of IPv4 (approximately 4 billion addresses), IPv6 was released in 1999. Though the two versions of IP have the same functionality, they differ in their structure and their capacity.
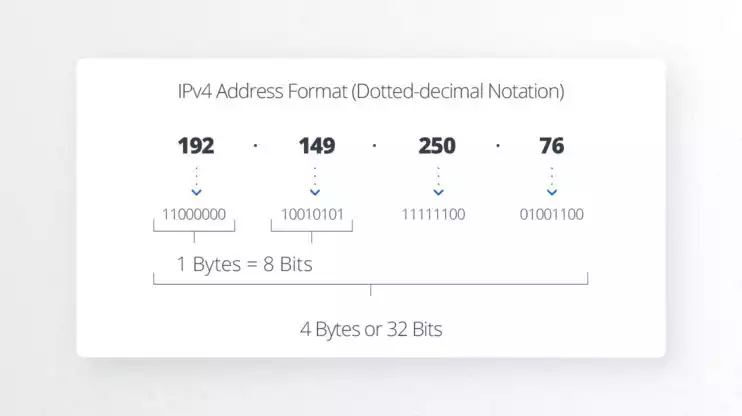
An IPv4 address consists of two parts, a network ID and a host ID. IPv4 addresses have four groups of numbers not exceeding the number 255, and are separated by decimals. The first three groups of the numbers identify the network, and the last group identifies the host. Each group of numbers in an IPv4 address has 8 bits, giving an entire IPv4 address 32 bits.
IPv6 addresses are structured differently in that they use alphanumeric combinations, have eight alphanumeric groups of four digits, are divided by a column, and each group consists of 16 bits, therefore, giving the IPv6 address 128 bits. If a group or some groups of the four digits are zeros, they may not be written, thus shortening the look of the IPv6 address. This increase in bits means that IPv6 will support a much, much larger number of addresses (approximately 3.4×1038). Besides the larger quantity, IPv6 allows for hierarchical addresses and route aggregation or the formation of a supernet. With this version of IP, we also see optimization of security and of service delivery.

IP addresses & website hosting
A domain name is the name of a website, for example, 10Web.io. IP addresses consist of a series of numbers that identify the hardware on which the domain exists. Many domains can share the same IP address, as in the case of shared hosting. Also, one domain can have several different IP addresses. Any time a request is sent for 10Web.io, a DNS resolver works to translate the human friendly domain name, into computer language, the IP address belonging to that specific domain and its content, origin, and destination. The request sent through your browser for the website 10Web.io is sent as a packet. In this packet, along with other data, are the sender’s IP address and the receiver’s IP address. This way, the data is confirmed, retrieved from the correct address, and delivered to the correct address.
Domains are hosted on servers. No matter the type of hosting, the server physically exists somewhere in the world. Like all hardware which is on the internet, these servers have IP addresses. IP addresses belonging to hosting servers are static, meaning that they don’t change. There are also dynamic IP addresses. These usually belong to network services and may sometimes change. When you host your website with your hosting provider, your domain will have the IP address of the physical server it is housed in. If you are using shared hosting, you will also be sharing the IP address with other websites that are hosted on the same server.
IP addresses are also used to point a domain to a hosting provider by adding an A record in the DNS records of the domain name provider. You may have purchased a domain name but may not have a live website yet. In order for your website to be live and on the internet, it has to be hosted. Once you have your hosting provider and the IP address of the server where your website will be hosted, you can go ahead and map your domain name to it.
IP addresses and WordPress
Taking into account that an IP address is the identifier of a domain, the device of a specific user, or any other device on the internet, there is a lot one can do with the information provided by the IP address. One of the key ways an IP address is used in WordPress, is security. By simply knowing the IP address of a user, you can give or restrict admin access to your WordPress website. You can prevent brute force attacks by setting up log in attempt limitations by IP. This allows for a set number of attempts from the same IP address. If the login limitation has been reached and login has failed, then the IP address is blocked to prevent a security breach. In WordPress you can also detect and display a user’s IP address. This will allow you to determine the location of your client or user, adding another layer of security. And lastly, WordPress allows you to block IP addresses to prevent your websites from spam, DDOS attacks, and getting hacked.
Proxies & reverse proxies
A proxy is basically a server that is placed immediately in front of the client’s hardware, before the internet, and before your original servers. Proxy servers have an IP address that is different from your original server IP. Your root server is where your website lives. In this way, proxy servers, or forward proxies, offer a layer of security and anonymity. Using proxies, you can enable access to certain websites and disable access to other websites.
A reverse proxy is a server that is placed in front of one or more servers to interrupt client requests coming to your root server in order to send and receive these requests itself. In doing so, the reverse proxy secures the root servers by assuring that it is the sole point of communication with the root servers. Reverse proxies allow for load balancing for sites with heavy requests and multiple servers by evenly distributing the requests and making sure to redirect the traffic to other servers in case a server has failed. They also load balance websites that have servers disbursed all over the world by detecting the closest geographical location of the request and sending it to the correct server.