What is Post in WordPress
Understanding how posts work in WordPress is essential for any blogger or website owner. In WordPress, a post refers to content that you publish regularly, like blog entries and news articles. These posts appear in reverse chronological order, with your latest content featured at the top, making them ideal for timely information.
Another key aspect of posts is their dynamic nature. They often have tags and categories to help organize the content, making it easier for your readers to find related articles. This organization can enhance your site’s navigation and keep your audience engaged.
Posts also foster reader interaction through comments. Engaging with your readers in the comment section can build a community and generate more interest in your blog. By understanding the role of posts, you can effectively share your stories, news, and updates with your audience.
Getting started with WordPress posts
Creating posts in WordPress involves navigating the Dashboard to add new posts, customizing content with the WordPress Editor, and managing media like images and videos. This guide will help you understand how to manage WordPress posts effectively.
Understanding WordPress posts
WordPress posts are a type of content primarily used for blog entries. They appear in reverse chronological order on your site, meaning the newest posts show up first. Posts can be organized into categories and tags, making it easy for readers to find related topics.
In addition, posts are syndicated through RSS feeds, allowing readers to subscribe and stay updated. Posts can also feature comments, encouraging interaction with your audience.
Creating your first WordPress post
To create your first post, log in to the WordPress dashboard. Navigate to Posts > Add new. This will take you to the WordPress Editor. As of WordPress 5.0, the Block Editor, also known as Gutenberg, is the default editor.
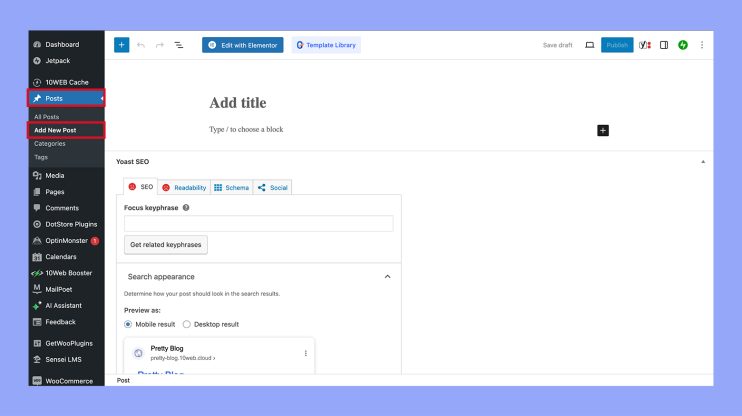
Start by entering a title in the box that says Add title. This is how your post will be identified. Below the title, you can start writing your content or add various blocks like images, videos, or custom HTML.
Post content and media management
In the WordPress Editor, content is created with blocks, making it easy to insert different types of media. You can add text, images, galleries, videos, and more. Use the Add media button to upload images or videos from your computer, or select from the media library.
For each post, you can set a featured image which will be the main image associated with your post. To publish your post, click the Publish button. You can also preview your post before publishing to ensure it looks just right. Managing post content and media in WordPress is straightforward once you get the hang of it.
Optimizing and managing posts
Optimizing and managing your WordPress posts involves organizing your content, enhancing visibility, and using effective publishing options. Understanding these elements will help you make your site more user-friendly and SEO-friendly.
Organizing your posts
To keep your posts easy to navigate, use Categories and Tags. Categories are broad groupings of your posts, like chapters in a book. Tags, on the other hand, are more specific, like keywords in an index.
For example, if you have a food blog, Categories could be “Breakfast,” “Lunch,” and “Dinner.” Tags might be ingredients or specific dishes. Always assign your posts to the right Categories and Tags to improve their structure and help visitors find related content easily.
Enhancing post visibility
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is key to making your posts easy to find online. Use a plugin like WordPress SEO by Yoast to optimize your titles, URLs (permalinks), and meta descriptions. This makes your content more attractive to search engines.
Include keywords naturally within your post. Add Featured Images and Excerpts to make your posts stand out in search results and on social media. Check your “Visibility” settings to ensure posts are Public, or if needed, set posts as Password Protected or Private.
Reviewing and updating posts regularly can also boost their performance. Use the Revisions feature to revert to earlier versions if necessary.
Post publishing options
When your post is complete, the Publish box in the WordPress editor offers several options. You can publish immediately or Schedule a future Published Date.
Scheduling posts allows you to manage when your content goes live, which is helpful for maintaining a consistent posting schedule.
You can also change the post’s Status to “Draft” if it’s not ready for publication. Preview your post before publishing it to see how it will appear to your audience. The Permalink or URL Slug should be clear and include important keywords.
Use Social Media integrations to share new posts automatically, broadening your reach.
Going beyond the basics
In this section, you’ll learn about more advanced WordPress post techniques and get a deeper look into the WordPress editing experience. We’ll cover custom post types, helpful plugins, and using different editors to enhance your posts.
Advanced WordPress post techniques
Custom post types are a great way to categorize your content beyond the default posts and pages. These allow you to create specific types of content, like portfolios or testimonials. You can register custom post types using a plugin or by adding code to your theme’s functions.php file.
Plugins can expand the functionality of your posts. For example, using the Advanced Custom Fields plugin lets you add custom fields to your posts. Custom fields can store additional data like ratings or product details, which can be displayed within your post template.
Widgets can also enhance your posts by adding extra functionality to your sidebar or other widget-ready areas. For instance, you might use a widget to display recent posts, categories, or even an author bio.
WordPress editing experience
The WordPress dashboard is where you’ll manage your posts. The editing screen can vary depending on whether you’re using the Classic Editor or Block Editor (Gutenberg).
In the Classic Editor, you have a simple, text-based interface. The Block Editor, on the other hand, offers a flexible experience where you can create content using blocks for paragraphs, images, videos, and more.
The WordPress database is where all your post data is stored. Understanding the structure of the database can help with troubleshooting and optimizing your site’s performance. Each post, including custom post types, is stored in the wp_posts table, with additional data in associated tables.
In conclusion, mastering WordPress posts is crucial for bloggers and website owners. Posts, which appear in reverse chronological order, help keep your content organized and engage readers through categories, tags, and comments. They enhance SEO and user interaction, making your site more dynamic and attractive. By effectively creating, optimizing, and managing posts, you can share your updates, improve search rankings, and keep your audience engaged, ultimately boosting your website’s success.