What is Classic Editor in WordPress
The Classic Editor in WordPress is a feature that many users still love. Before the Gutenberg editor came along, this “what you see is what you get” (WYSIWYG) editor was the default tool for creating and editing posts.
The Classic Editor allows you to format your content using familiar, straightforward tools, just like a simple word processor. Many users prefer it for its simplicity and ease of use.
The introduction of Gutenberg brought a new way to edit with blocks, making the editor more modern but also more complex.
While some users appreciate the flexibility of the block editor, others find it overwhelming.
If you prefer a more traditional experience, Classic Editor is still available as a plugin. This lets you stick to the old way of doing things without navigating the new layout.
You can easily switch back to the Classic Editor if you miss the old interface. This plugin lets you continue using plugins that rely on the classic layout and offers a smooth, less cluttered writing space. For those who want a simple, no-frills editing experience, the Classic Editor remains a popular choice.
Understanding classic editor in WordPress
The Classic Editor was the main way to create and edit content in WordPress for many years.
In December 2018, WordPress 5.0 brought the launch of a new editor called Gutenberg. Gutenberg introduced a block-based approach, making it easier to create complex layouts without coding. Many users liked the new features, but others missed the simplicity of the Classic Editor.
Those who preferred the old way had the option to switch back by using a plugin. This shift represents a significant change in how WordPress handles content creation.
Common issues with Gutenberg
With Gutenberg, some users faced challenges adapting to the new interface. The block system was different from the traditional text editor.
Some found it less intuitive, which affected their workflow.
Plugin compatibility: Some plugins did not work well initially with Gutenberg, which caused compatibility issues.
Learning curve: Users who were used to the Classic Editor had to invest time in learning how the new editor worked. This adjustment period was not always smooth.
Performance issues: Certain users reported slow performance, especially when working with large content pieces.
Classic editor plugin features
The Classic Editor plugin allows users to revert to the previous editing experience. Here are some key features:
Simple interface: The Classic Editor has a straightforward, text-based interface which many find easier to use.
Compatibility: It works seamlessly with older themes and plugins that might have issues with Gutenberg.
User control: Administrators can set the default editor for all users and allow users to switch between editors.
Meta boxes: Custom meta boxes that were added in older versions of WordPress are fully supported.
The plugin ensures that users who prefer the old editing style can continue to use it without losing functionality.
How to install and activate the classic editor plugin
You need to install and activate the Classic Editor plugin to return to the WordPress’ classic editor interface. Follow these steps to get started.
First, you need to log in to your WordPress admin panel. This is usually found at yoursite.com/wp-admin.
Once logged in, navigate to the Plugins section on the left sidebar. Click on Add New.
In the search bar, type Classic Editor and press Enter.
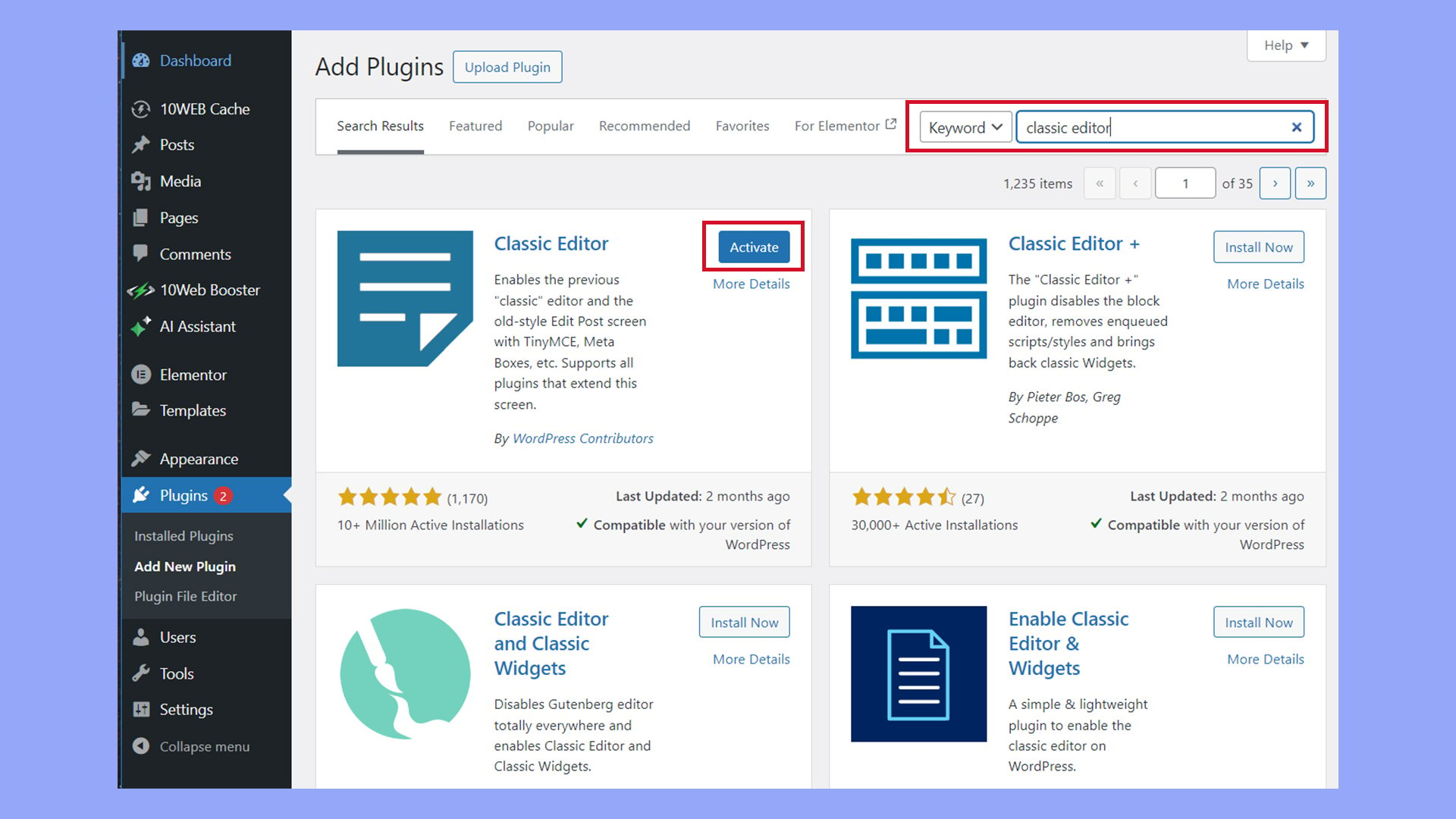
You should see the Classic Editor plugin in the search results. Click on the Install Now button next to it. Wait a few seconds until the plugin is installed.
When the plugin is ready, the Install Now button will change to a blue Activate button. Click this button to activate the plugin.
Activation and configuration
After activating the plugin, you need to configure some settings. Go to Settings in your dashboard’s left sidebar and click on Writing.
Here, you’ll find options to make the Classic Editor the default for all users. Additionally, you can choose to allow users to switch editors if they prefer.
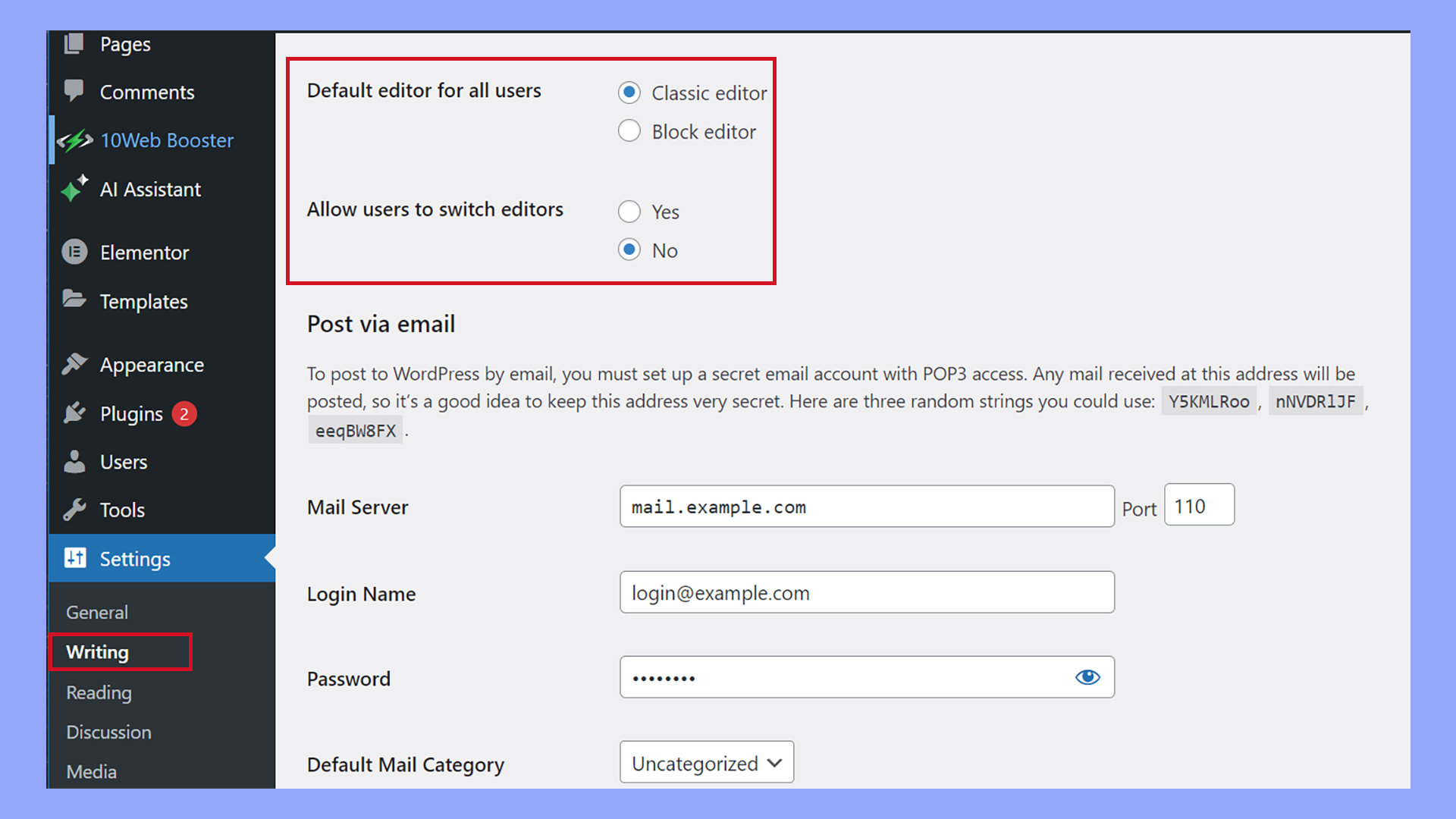
Make sure to save any changes you make by clicking the Save Changes button at the bottom of the page.
By following these steps, you’ll restore the classic WordPress editor for your site. This ensures consistency and compatibility with any plugins that rely on the old editor interface.
Working with the classic editor in WordPress
When using the Classic Editor in WordPress, you’ll interact with features like creating and editing posts, as well as various toolbars and options for formatting content.
Creating and editing posts
In the Classic Editor, creating and editing posts is straightforward. First, navigate to Posts > Add New in your WordPress dashboard.
You’ll see a screen resembling a word processor, which uses TinyMCE for editing.
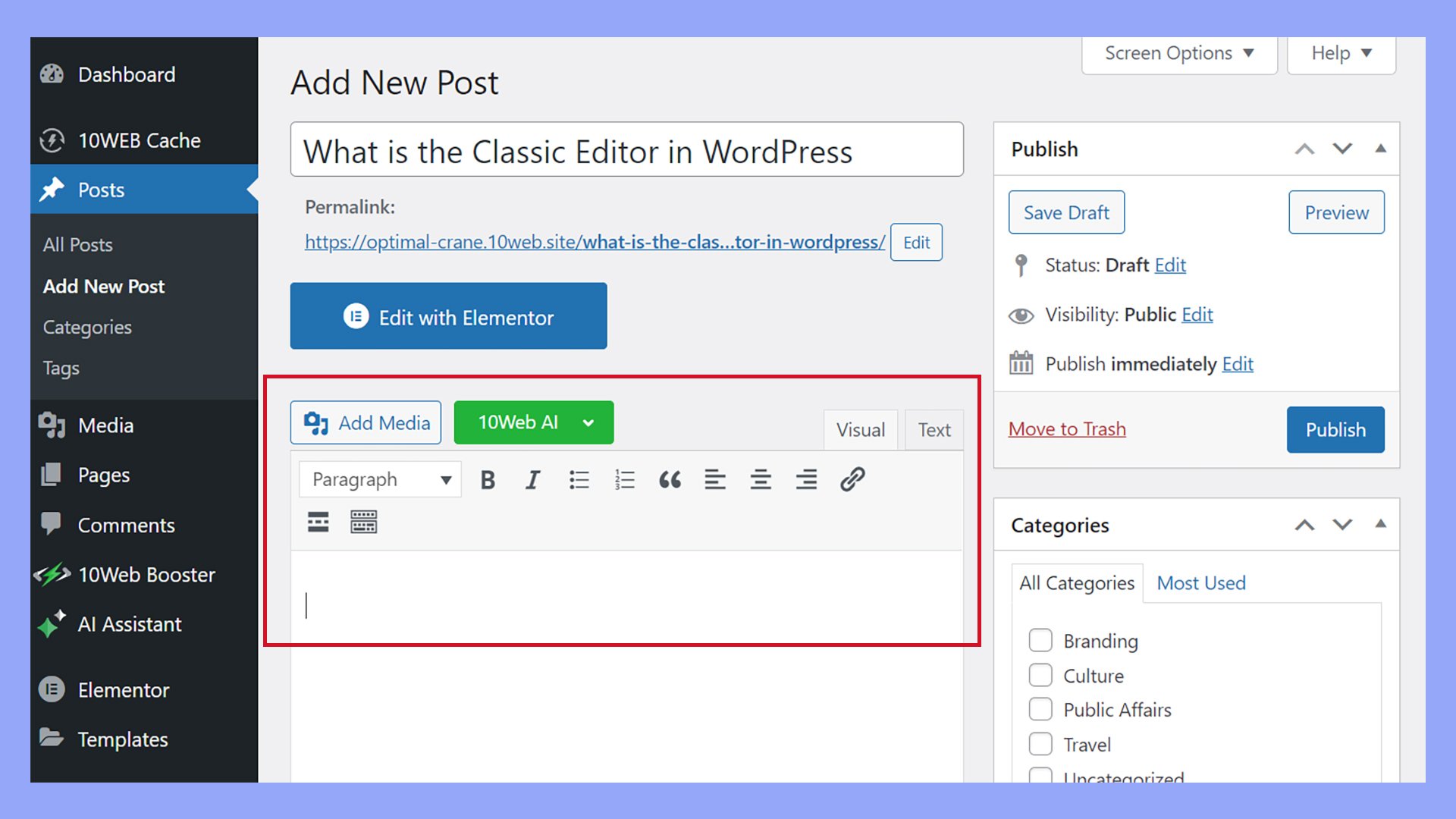
You can enter the title of your post at the top and begin writing in the main content area below. The editor has options for adding bold, italic, and other text styles.
To include media, use the Add Media button above the toolbar. You can upload images, create galleries, and embed videos. Once you’ve finished, press Publish or Update to save your work.
Using toolbars and options
The toolbars in the Classic Editor offer many formatting and editing options. Here are some key features you’ll find:
- Bold: Make your text bold by selecting it and clicking the B button.
- Italic: Similarly, use the I button for italic text.
- Links: Add hyperlinks by selecting text and pressing the link button.
The toolbar also includes options for creating lists, adjusting text alignment, and inserting quotes.
Clicking the toolbar toggle displays additional options for formatting content, including changing the text color.
There is a Text tab that allows you to switch to HTML view if you need to edit the code directly. For more advanced options, plugins can extend the Classic Editor’s capabilities, adding extra toolbars or features to your editing experience.
Tips for using the Classic Editor in WordPress
Power users can customize the Classic Editor to enhance its functionality.
- Plugins: Use additional plugins to add features like shortcodes and custom fields.
- Filters: Apply filters such as
classic_editor_enabled_editors_for_postandclassic_editor_enabled_editors_for_post_typeto control when to use the Classic Editor. - CSS customization: Modify the editor’s appearance using custom CSS.
By using these options, you can tailor the Classic Editor to better suit your specific needs and preferences.
Classic Editor for developers
Developers can leverage the Classic Editor to integrate custom code and advanced functionalities.
- Custom plugins: Write custom plugins to extend the capabilities of the editor.
- GitHub resources: Use open-source projects on GitHub to find and share code snippets.
- Code snippets: Insert custom HTML, CSS, and JavaScript directly into your posts.
Understanding how to manipulate the Classic Editor through filters and hooks gives developers greater control over the content management process.
Benefits and considerations when switching editors
The WordPress Classic Editor is appreciated for its ease of use, straightforward interface, and compatibility with various plugins. However, it’s important to weigh these benefits against the challenges of switching between editors.
User-friendliness and compatibility
The Classic Editor in WordPress offers a simple and intuitive interface. If you’re familiar with text editors like Microsoft Word, you’ll find it easy to use. This makes it a great choice for users who want to create content quickly without learning new tools.
The editor allows you to format content in place and integrates smoothly with many WordPress plugins. This compatibility ensures that features like SEO tools and custom fields work seamlessly. You can also extend its functionality with additional plugins.
Another plus is its stability. Since it’s been around for a while, most bugs have been worked out, making it a reliable choice. For those used to the Classic Editor before the introduction of Gutenberg, it provides a sense of familiarity and comfort.
Considerations for switching between editors
Switching between the Classic Editor and another editor like Gutenberg can be disruptive. You might lose custom formatting or face issues with plugins that are optimized for one editor but not the other.
You need to consider the learning curve. Though the Classic Editor is easy to use, moving to Gutenberg might require you to spend time learning a new interface. This can slow down your workflow initially.
Compatibility issues are also important. If you heavily rely on plugins tailored for one editor, switching can lead to plugin conflicts or require additional adjustments to make everything work smoothly.
Finally, consider your content needs. While the Classic Editor is great for simple text-based content, Gutenberg offers more advanced layout options. If your content strategy evolves, you might find the Classic Editor limiting.
In summary, the simplicity and familiarity of the Classic Editor in WordPress have made it a favorite. It’s especially useful for those who prefer a straightforward editing experience.
Even though WordPress has introduced the Block Editor, known as Gutenberg, many users still choose the Classic Editor. It continues to be supported through plugins, ensuring that those who prefer it can still use it.
No matter your choice, WordPress offers flexibility. The Classic Editor remains an option for those who find it suits their needs better.