What Is WordPress Backend
The WordPress backend is the administration area where you can manage users, create content, and customize your site’s appearance and settings. The backend of WordPress is crucial for anyone who wants full control over their site.
In the backend, also known as the admin area or Dashboard, you will have access to various tools that make managing your site easier. You can install plugins, adjust settings, and monitor site analytics, all in one place. Only logged-in users with appropriate permissions can access this area, ensuring your site remains secure.
The WordPress backend is where the magic happens. As the content management hub, it allows you to design your site, schedule posts, and collaborate with other users. While visitors interact with the frontend, your work in the backend shapes their experience. Dive in to discover how mastering the backend can transform your WordPress site.
Getting started with the WordPress backend
The WordPress backend allows you to manage the content, users, settings, and plugins of your site. Knowing how to access and navigate this area is essential for running your website smoothly.
Understanding the admin dashboard
When you first log in to WP-Admin, you will see the Admin Dashboard. This main screen provides a snapshot of your site’s activity.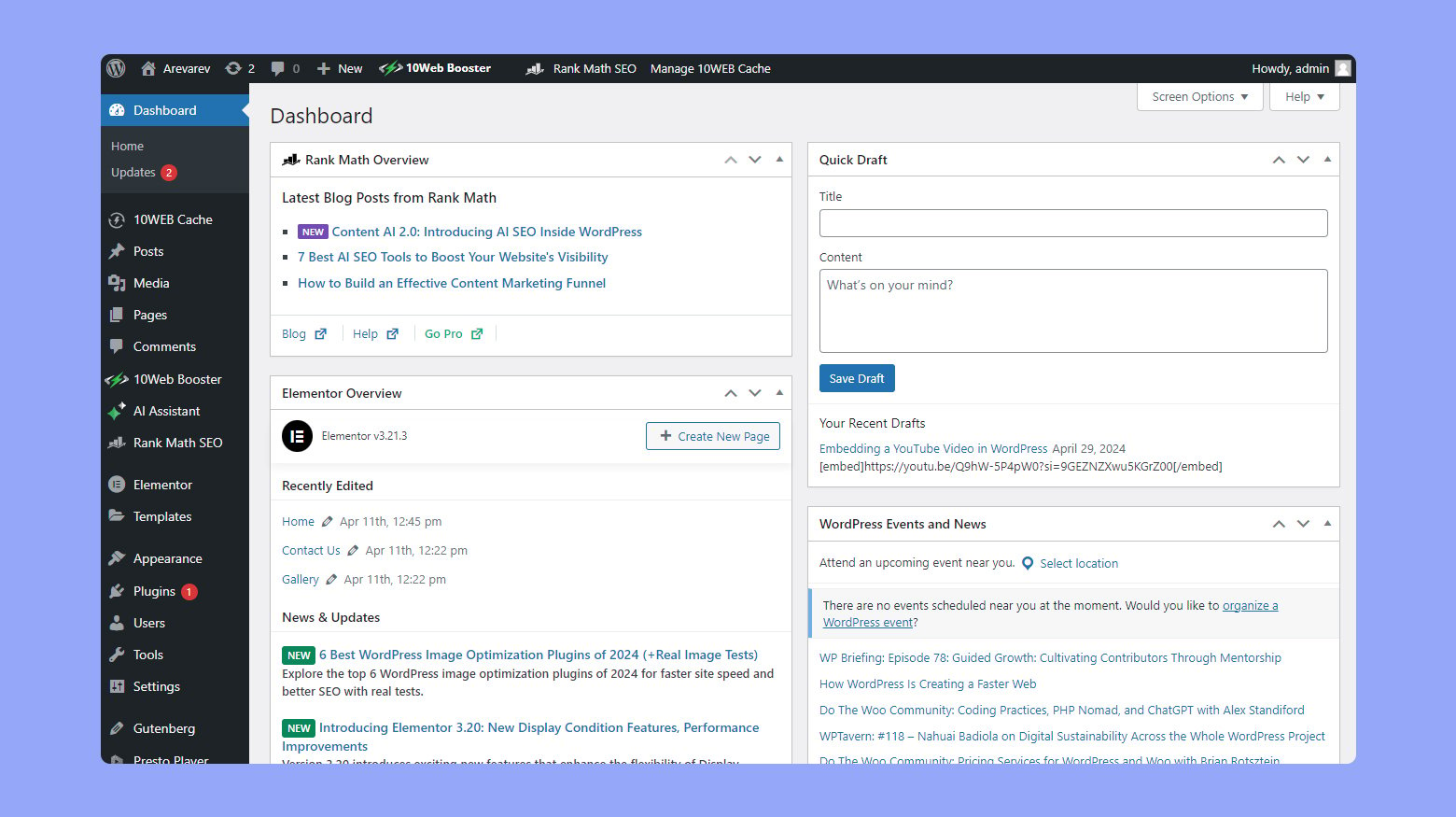
It includes widgets for updating your content, checking site stats, and accessing recent comments. You can customize this dashboard by dragging and dropping widgets or using the Screen Options menu at the top.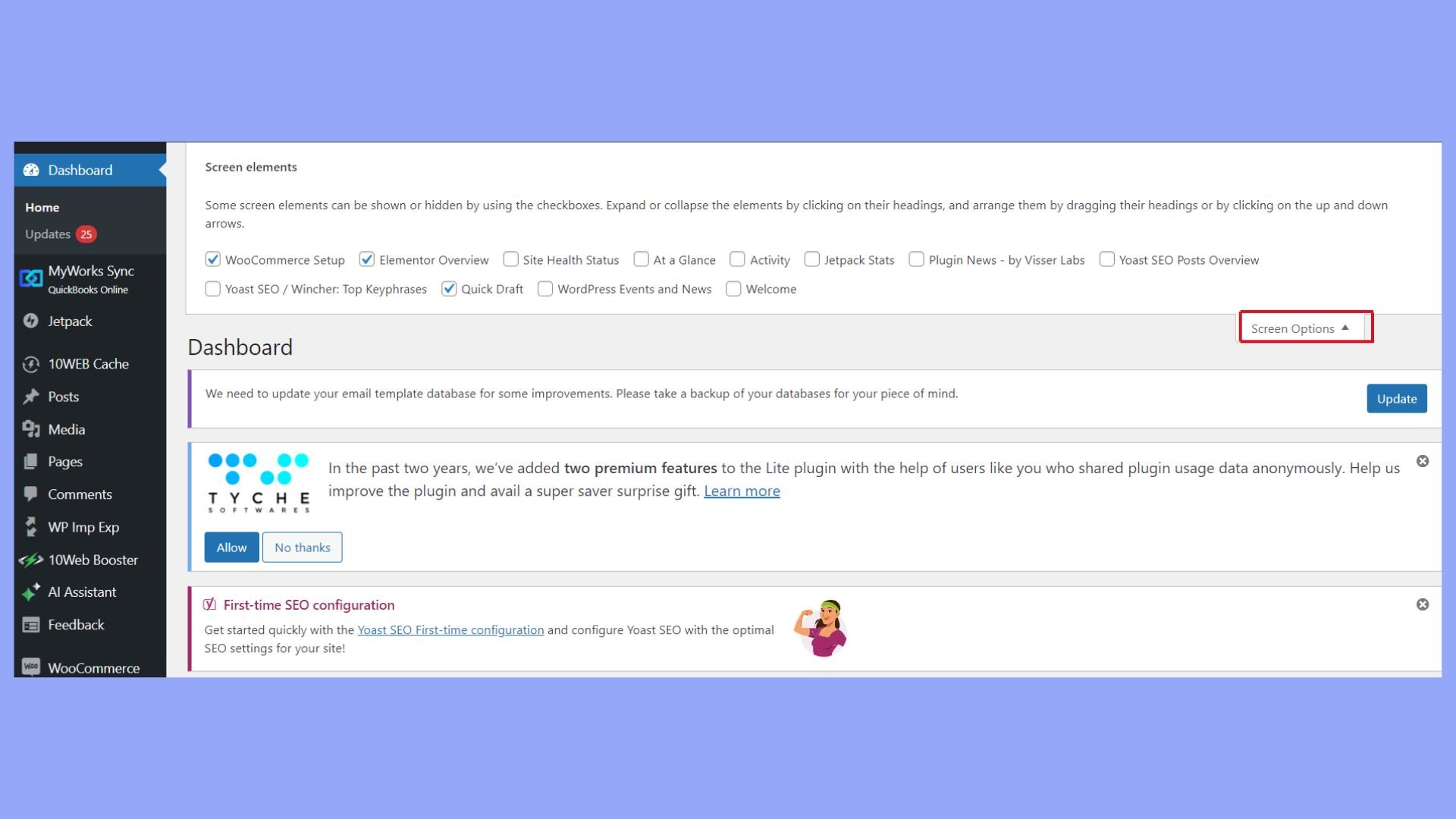
Important sections to note:
- At a glance is the overview of your site’s content, including the number of posts and pages.
- Activity refers to the recent posts and comments.
- Quick draft is a space to quickly draft new posts.
Logging in to WP-admin
To access the backend, you need to log in to WP-Admin. To do so, go to yoursite.com/wp-admin and enter your username and password. If successful, you will be redirected to the Admin Area. If you forget your password, you can use the Lost your password? link to reset it.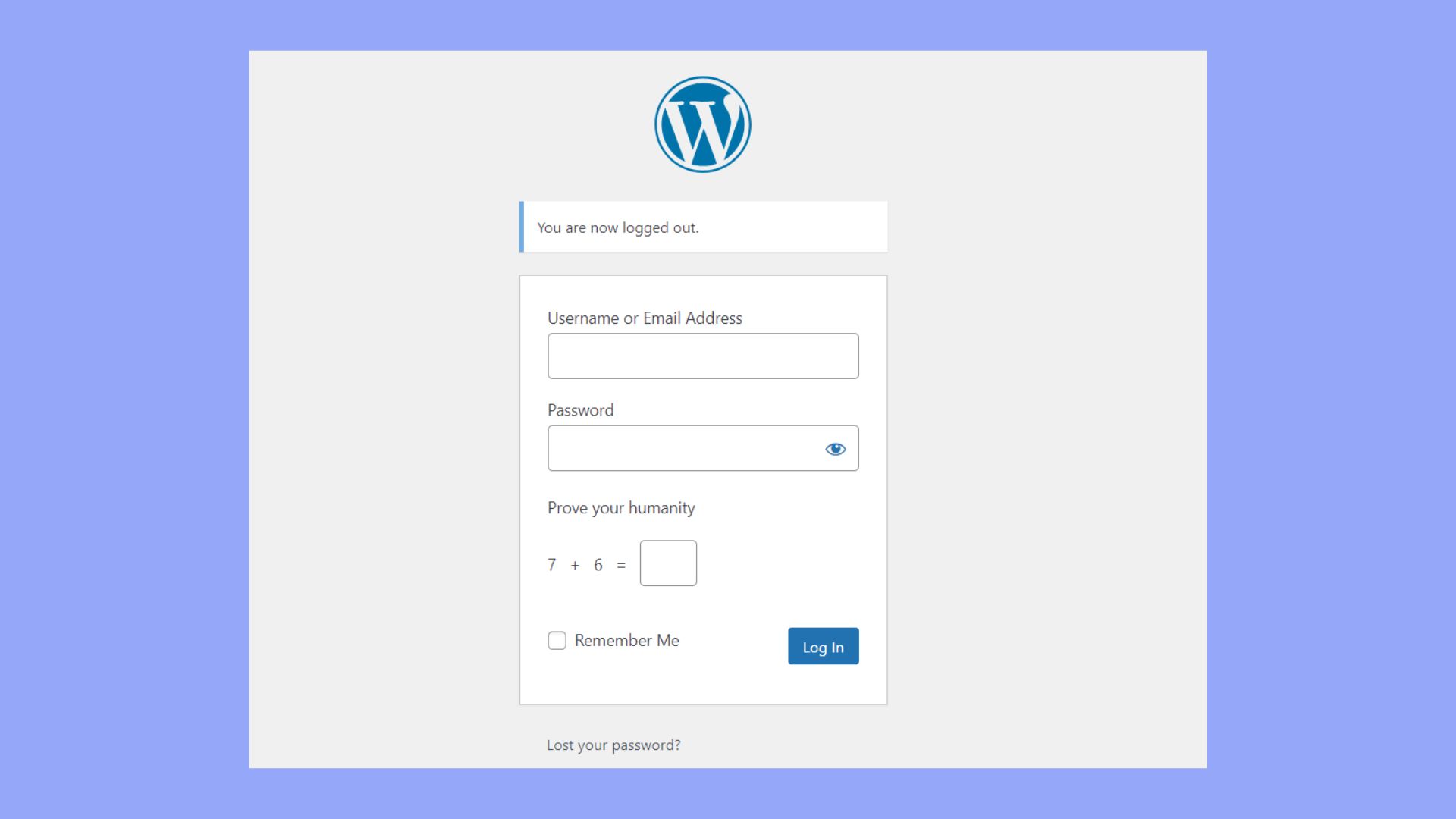
Exploring the admin toolbar
Once logged in, you will see the Admin Toolbar at the top of the screen. This toolbar provides quick access to various important functions.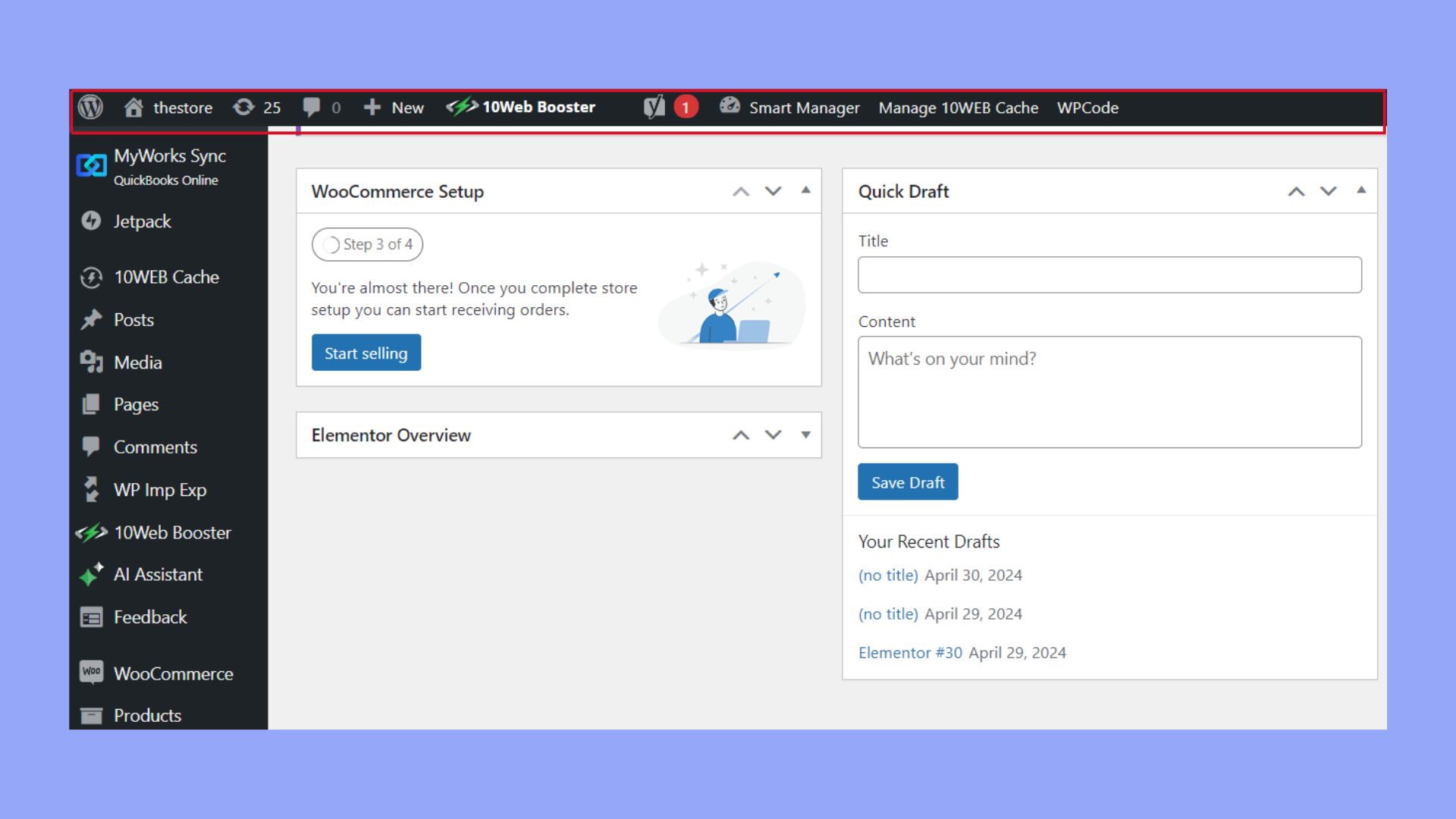
Here are brief descriptions of the key elements found in the WordPress Admin Toolbar and their purposes:
- My Sites: This option is for users who manage multiple WordPress sites, allowing easy navigation between them. (Not visible in the screenshot, since I have one website)
- New: Enables the creation of new posts, media, pages, and more, streamlining content addition.
- Comments: Provides a dedicated section to monitor and manage comments left on your site.
- Edit Profile: Offers access to modify your user profile settings.
- View Site: Serves as a direct link to view your site as it appears to the public.
Take advantage of these shortcut links to perform tasks faster and keep an eye on your site’s status. The admin toolbar is always available no matter where you are in the backend.
Managing content and media
When using WordPress, the backend is where you control your content and media. This section covers how to create and edit posts, manage your media library, and organize pages and categories efficiently.
Creating and editing posts
On the WordPress backend, you can create and edit posts easily. To start, go to the Posts section. Here, you will find options to add a new post or edit existing ones.
When creating a new post, you can write your content in the editor. The editor allows you to format text, add headings, and insert links. You can also use Custom Fields to add extra information.
Don’t forget to add tags and select categories to organize your posts. This helps visitors find related content on your site. Lastly, you can save your post as a draft or publish it immediately by clicking the relevant button.
Handling media library and uploads
Managing your media files is simple with the WordPress Media Library. To access it, go to the Media section. Here, you can upload, organize, and search for files like images, videos, and documents.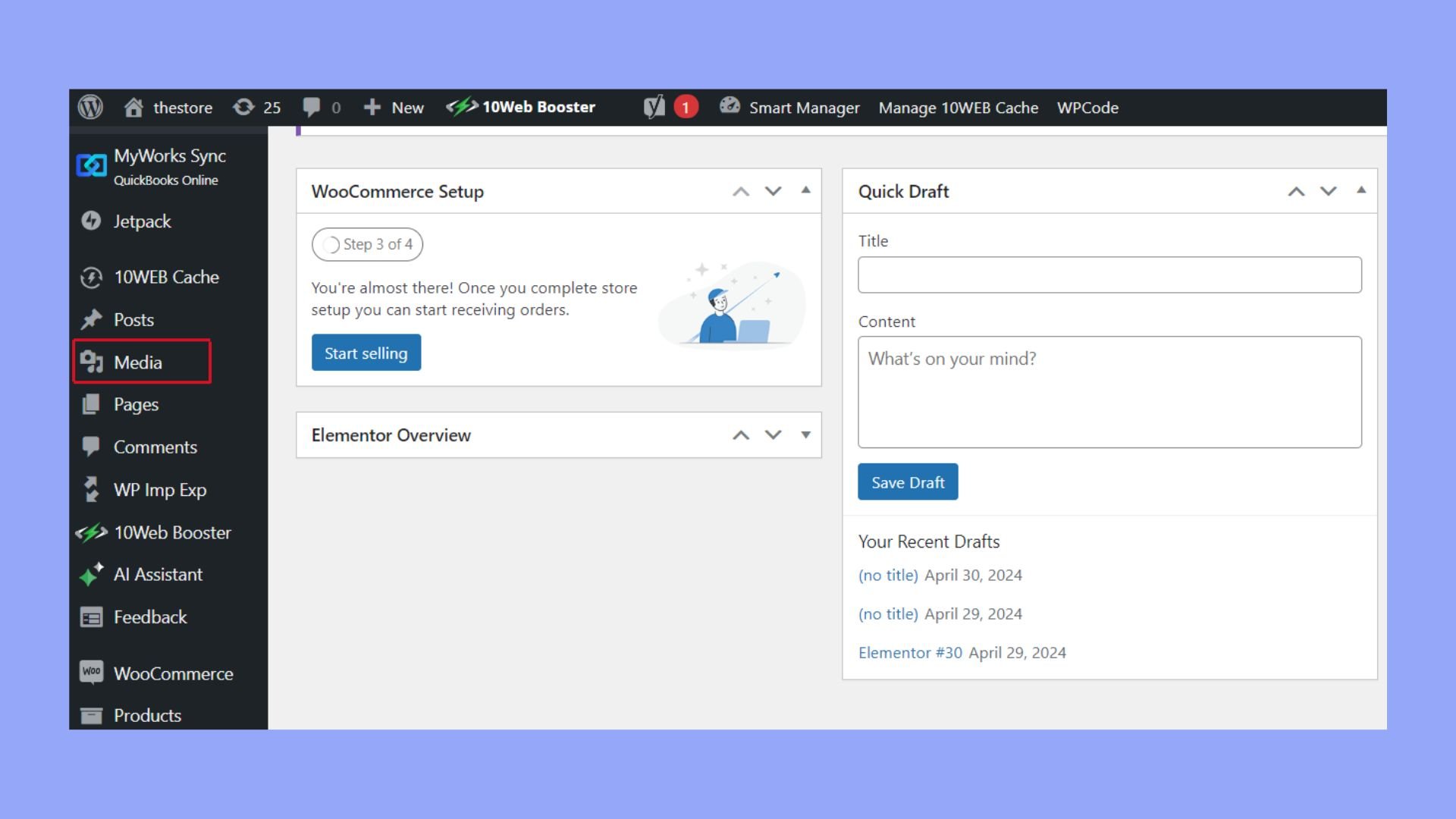
Uploading files is straightforward. Click the Add New button, then drag and drop your files or select them from your computer. All your uploaded media will be listed in the library. You can edit media details, like the title, alt text, and description, directly from the library. This makes it easier for search engines to index your media and improves your site’s accessibility.
Organizing pages and categories
In WordPress, creating and managing pages is much like handling posts. To add a new page, go to the Pages section and click Add New. Pages are typically used for static content like About, Contact, or Services.
You can also organize your content using Categories. Categories help group related posts together, making it easier for users to navigate your site. To manage categories, go to Posts > Categories.
You can create new categories and assign them to your posts. This structure improves your site’s organization and helps visitors find content quickly. You can also use subcategories for more detailed organization, which further enhances user experience.
Customization and themes
WordPress offers various ways to customize your website’s backend to fit your needs. From selecting themes designed to improve the look and feel, to widgets and menus that add functionality, achieving a customized backend is straightforward with the right tools.
Selecting and installing themes
Themes give your WordPress site its look and feel. To start, go to the Appearance section in your dashboard and select Themes. Here, you can browse free themes from the WordPress theme repository or upload a premium theme by clicking Add New and then Upload Theme. Choose the theme .zip file from your computer and install it. Active themes immediately apply their design across your site.
Customizing themes and appearance
Once you have a theme, tweak its appearance to match your brand. Go to Appearance > Customize. This will open the WordPress Customizer where you can change the color scheme, fonts, and layout. Some themes offer more customization options than others. Additionally, you can add custom CSS for specific styling needs. Feel free to adjust different sections such as the header, footer, and sidebar to make your website unique.
Using widgets and menus
Widgets are small blocks that add specific content or features to your site. These could be for adding a search bar, recent posts, or social media icons. To manage widgets, go to Appearance > Widgets. Drag and drop widgets into different areas of your site like sidebars or footers. Menus help in organizing your site’s navigation. You can create custom menus by going to Appearance > Menus. From there, decide what pages, categories, or custom links to include. Drag items to change their order and create dropdown lists for sub-menus. By effectively using themes, customization options, widgets, and menus, you can control both the aesthetics and functionality of your WordPress backend.
Plugins and extensions
Plugins and extensions enhance your WordPress backend by adding new features and functionalities. This section will guide you on how to find, install, and manage plugins effectively, allowing you to customize your website according to your needs.
Finding and installing plugins
To find plugins, go to your WordPress admin area. Click on Plugins in the menu, then select Add New. You can search for plugins using keywords or browse through categories. Once you find a plugin you like, click Install Now. After installation, click Activate to enable the plugin on your site.
You can also find the plugins you need by exploring 10Web’s plugin repository. For premium or custom plugins, you’ll need to install and activate it to get the added features working.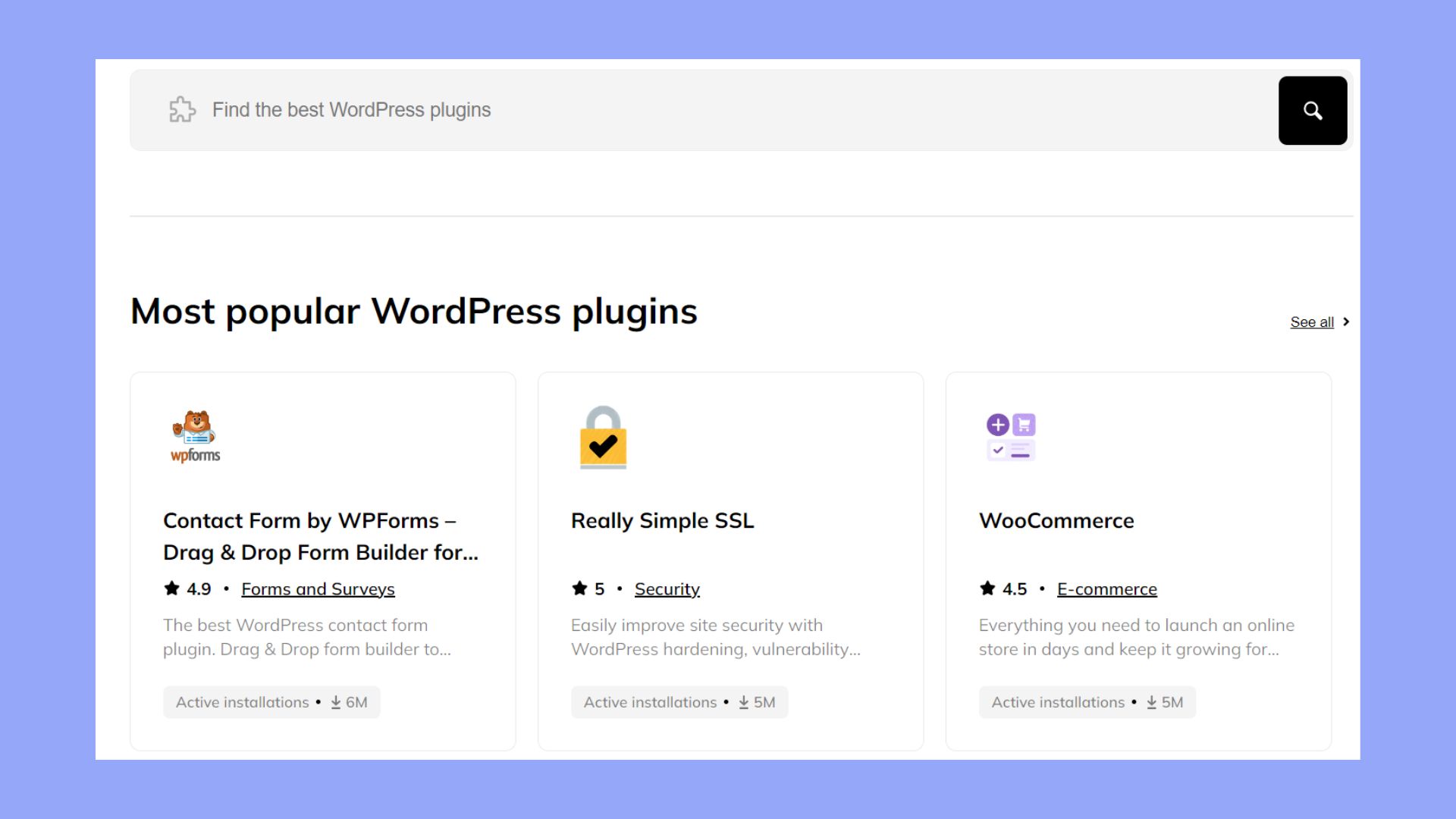
Managing plugins and custom functionality
Managing plugins is key to maintaining an efficient website. In the Plugins section of your admin area, you can see all installed plugins. Here, you can activate, deactivate, or delete them as needed.
To update a plugin, check for notifications in the Plugins menu. Keeping plugins updated ensures security and compatibility with your WordPress version.
Custom functionality can be achieved by using plugins designed for specific tasks, like SEO, security, or social media integration. For instance, a branding plugin can help you add custom logos and stylings to your admin dashboard.
Stay organized by regularly reviewing your plugins and deactivating any that are no longer needed to keep your site running smoothly.
In conclusion, mastering the WordPress backend is essential for efficiently managing and customizing your website. From creating and scheduling content to installing plugins and adjusting settings, the backend offers a comprehensive toolkit that empowers you to shape a unique and engaging user experience, making it a fundamental aspect of website administration.