If you run an ecommerce business, understanding payment gateway fees is important for keeping costs in check and ensuring long-term profitability. These gateways ensure secure, easy transactions, but they also come with charges you should know about—like transaction fees, setup costs, monthly subscriptions, and even penalties for things like disputes or international sales.
In this article, we’ll explain the different types of fees you may encounter, from per-transaction charges to hidden costs, and how factors like transaction volume, business type, and risk can affect what you pay. As ecommerce opens doors to a global audience, knowing how to deal with these fees is essential for maximizing your profits in the marketplace.
FAQ
How much do payment gateways charge per transaction?
How do I avoid payment gateway charges?
What is a typical gateway fee?
Which payment gateway has the lowest fees?
What is a payment gateway?
A payment gateway is a technology that lets businesses accept card payments from customers. It connects a merchant’s website or store to the banks that handle payments. When you buy something online, the payment gateway collects your card details. It then sends this information to the bank in a safe way. This happens behind the scenes in just seconds.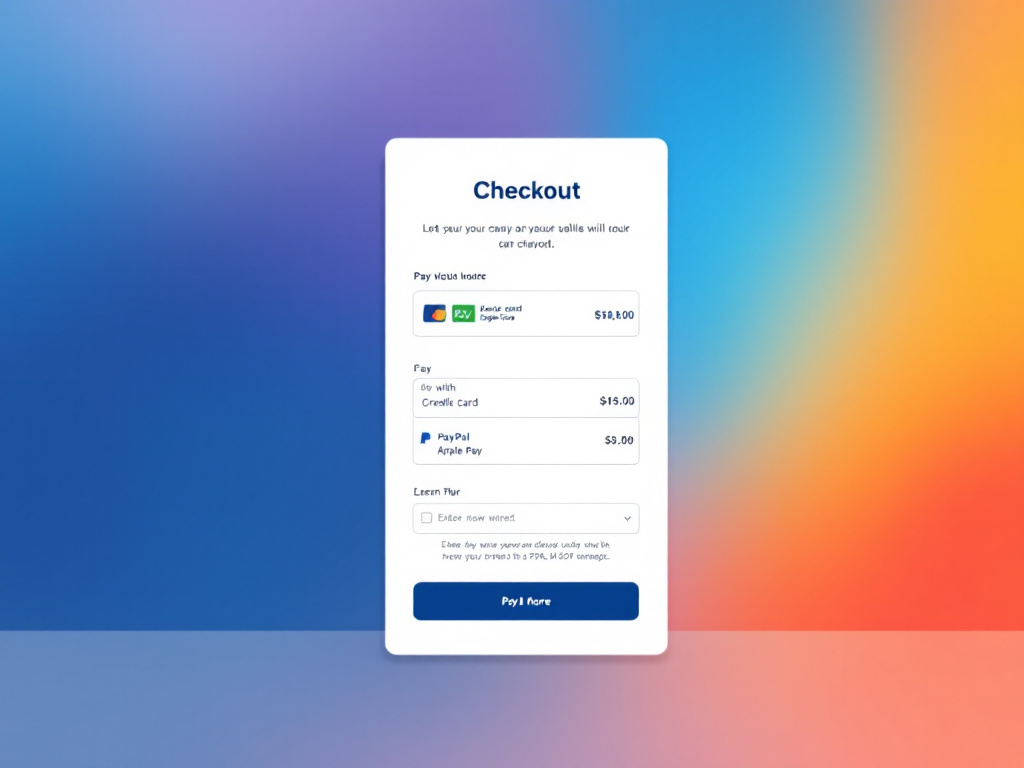
Payment gateways come in two main types:
- Physical card readers in stores
- Online portals for websites and apps
These gateways handle different payment methods, like:
- Credit cards
- Debit cards
- Digital wallets (e.g. PayPal)
For online stores, the payment gateway shows up as the checkout page. It’s where you enter your card number and other payment details. The gateway keeps your information safe as it moves between you, the store, and the banks. This helps prevent fraud and protects your sensitive data.
Businesses need a payment gateway to take card payments. It’s a key part of selling goods or services, both online and in physical stores.
Looking to sell online? Develop and launch your store with 10Web AI Ecommerce Website Builder.
Create your online store in minutes!
What are payment gateway charges?
Payment gateway charges are fees businesses pay to process online payments. These charges cover the costs of securely handling transactions and transferring money between customers and merchants.
Types of payment gateway fees
When choosing a payment gateway, understanding the different types of fees is essential to accurately budgeting your transaction costs. Here’s a breakdown of common payment gateway fees:
- Setup fees: One-time costs incurred when you initially sign up with a payment gateway. While some providers charge setup fees, others may offer this service for free.
- Transaction fees: Charged for each payment processed through the gateway, typically including a percentage of the transaction amount plus a fixed fee. For example, you might pay 2.9% + $0.30 per transaction.
- Monthly fees: Recurring charges that some payment gateways require for continued service usage. Not all providers charge monthly fees, so it’s worth checking.
- Chargeback fees: Fees are applied when a customer disputes a transaction, often ranging between $15 to $25 per chargeback. This helps cover the administrative costs associated with managing disputes.
Factors influencing payment gateway fees
When evaluating payment gateway fees, several factors can influence the overall costs associated with processing transactions. Here are the primary aspects to consider:
- Payment method: The type of payment method used can affect fees significantly. For example, credit card transactions often come with higher processing costs than debit cards or bank transfers.
- Transaction volume: Many gateways offer tiered pricing based on volume, where processing a higher number of transactions per month can lead to lower per-transaction fees.
- Business type and risk level: Industries considered high-risk, such as gambling or certain e-commerce sectors, may incur higher fees due to a greater likelihood of chargebacks or fraud.
- Features and support: Additional features like advanced fraud protection and 24/7 customer support can impact costs, with more comprehensive services generally leading to higher fees.
- Location: The geographical location of transactions also matters; domestic transactions tend to be cheaper than international ones due to reduced cross-border processing expenses.
What are common fee structures?
Payment gateways use different fee models to charge for their services. These structures can affect how much you pay for processing transactions.
Flat fee model
This model charges the same rate for all transactions. You pay a set percentage plus a fixed amount per transaction. For example, a gateway might charge 2.9% + $0.30 for each sale.
This is simple to understand. You don’t have to worry about different rates for different card types. It’s good for businesses that want easy-to-predict costs. But flat fees can be more expensive for some transactions. Larger sales may cost more than with other models.
Tiered pricing structure
This model groups transactions into tiers. Each tier has its own rate. The tiers are often based on the type of card used. Qualified transactions get the lowest rates. These are usually standard credit card purchases. Mid-qualified and non-qualified transactions cost more. These might include rewards cards or business credit cards.
Tiered pricing can save money on some transactions. But it can be hard to guess your total costs. You might pay high fees for premium cards. Some gateways offer volume discounts. As your sales grow, your rates may go down. This can help bigger businesses save money.
Payment gateway charges and fees
Understanding the various charges and fees associated with payment gateways is essential for budgeting and selecting the right provider for your business. Here’s a breakdown of common charges to consider.
Transaction fees
Payment gateways charge fees for each transaction they process. These fees can vary based on the type of transaction and payment method used. Let’s look at the main types of transaction fees you’ll encounter.
Per-transaction charges
Most payment gateways charge a percentage of the transaction amount plus a fixed fee. For example, Stripe charges 2.9% + $0.30 for domestic card transactions. This means if you sell a $100 item, you’ll pay $3.20 in fees.
Fees may be higher for:
- Manual card entry (+ 0.5%)
- International cards (+ 1.5%)
- Digital wallets
Some gateways have flat fees instead of percentages. These can be good for high-value transactions but may cost more for small purchases.
Batch processing fees
Batch processing involves grouping multiple transactions to process them all at once. This can save time and money compared to processing each transaction separately. Some gateways charge a fee for each batch, while others include it in their monthly fees. Batch fees are often a flat rate, like $0.25 per batch.
Benefits of batch processing:
- Lower per-transaction costs
- Faster settlement times
- Easier reconciliation
Keep in mind that batching can delay when funds hit your account. Some businesses prefer real-time processing for quicker access to their money.
Recurring costs
Payment gateways often have ongoing fees beyond just per-transaction charges. These regular costs can add up over time and impact your bottom line.
Monthly account fees
Some payment gateways charge a flat monthly fee to keep your account active. This fee can range from $10 to $100 or more. The exact amount depends on your sales volume and the features you need.
Stripe and PayPal don’t charge monthly fees for basic accounts. But their advanced plans with extra tools do have monthly costs. For example, Stripe’s premium plan starts at $59 per month. Before signing up, check if the gateway offers a free trial period. This lets you test the service without paying monthly fees right away.
Annual maintenance charges
Yearly fees are less common but still exist with some providers. These cover things like PCI compliance checks and account updates.
Annual fees can be $100-$300 or more. They’re often charged all at once, which can be a big hit to your budget. Some gateways waive annual fees if you process enough sales volume. Others build the cost into their monthly fees instead of charging separately.
Ask potential providers about all recurring costs upfront. This helps you avoid surprises and pick the best option for your budget.
Incidental fees
Payment gateways may charge extra fees beyond the basic rates. These can add up if you’re not careful.
Chargeback expenses
A chargeback happens when a customer disputes a charge with their bank. If this occurs, you may have to pay a fee. This fee can range from $15 to $100 per case. The exact amount depends on your payment provider.
Chargebacks are costly. You lose the sale and the product. You also pay the chargeback fee. To avoid these, keep good records. Make sure your business name shows clearly on credit card statements. Give refunds when asked.
Penalty fees
Payment gateways may charge penalty fees for certain actions. These can include:
- Missed payments
- Bounced checks
- Account freezes
- Excessive chargebacks
Penalty fees vary by provider. They can be $25 or more per incident. Some gateways charge higher fees for repeat offenses. To avoid penalty fees, follow the rules set by your gateway. Pay your bills on time. Keep your chargeback rate low. Make sure you have enough money in your account for payments.
International transaction charges
Payment gateways often add extra fees for transactions across borders. These can include currency conversion and cross-border charges. Let’s look at the main types of international fees you might face.
Currency conversion fees
When you buy something in a foreign currency, your payment gateway may charge a fee to change your money. This fee is usually a percentage of the transaction amount. It can range from 1% to 4% on top of the exchange rate.
For example, if you buy a €100 item with US dollars, you might pay:
- €100 x current exchange rate
- Plus 2-3% conversion fee
Some gateways build this fee into their exchange rates. Others list it as a separate charge. To save money, look for gateways with lower conversion fees or better exchange rates.
Cross-border transaction fees
Cross-border fees apply when the buyer and seller are in different countries. These fees cover the extra costs and risks of international sales. They’re usually a flat fee plus a percentage of the sale.
Common cross-border fees:
- 0.5% to 2% of transaction value
- $0.30 to $0.80 per transaction
For a $100 sale, you might pay:
- $1.50 (1.5% fee)
- Plus $0.50 (flat fee)
To reduce these costs, look for payment gateways that specialize in global transactions. Some offer lower fees for certain country pairs or high-volume sellers.
Security and compliance costs
Payment gateways need strong security to protect transactions. This costs money. Two big expenses are PCI compliance and SSL certificates.
PCI compliance fees
PCI compliance means following rules to keep credit card data safe. Payment gateways must meet these standards. The costs can vary:
- Yearly fees: $60 to $180 for small businesses
- Monthly fees: $5 to $25
- One-time setup fees: $50 to $200
Some gateways include PCI compliance in their base price. Others charge extra. You may need to pay for yearly scans of your systems. These can cost $100 to $500 per scan.
SSL certificate expenses
SSL certificates encrypt data between a website and its visitors. They’re a must for payment gateways. Costs depend on the type:
- Domain Validation (DV): $10 to $70 per year
- Organization Validation (OV): $100 to $500 per year
- Extended Validation (EV): $200 to $1000 per year
Many gateways provide a basic SSL certificate. But you might want a higher-level one for more trust. You’ll need to renew your SSL every 1-2 years. Some gateways charge for this. Others include it in their fees.
Integration and setup fees
Payment gateways often charge fees to set up and link their systems with your business. These costs can vary based on the provider and how complex the setup is.
One-time setup costs
Many payment gateways ask for a one-time fee to create your account and get you started. This fee can range from $25 to $250. Some providers don’t charge anything for basic setups. The cost often depends on:
- How complex your needs are
- What features you want
- The size of your business
You might pay more if you need special tools or have a big company. Smaller businesses or those with simple needs may pay less or nothing at all.
Payment gateway integration charges
Linking a payment gateway to your website or app can cost extra. This is called integration. The price can change based on:
- How hard it is to add the gateway to your site
- If you need help from experts
- What type of system you use
Some gateways offer free plugins for common platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce. Others might charge $100 to $500 for more complex setups. If you need a custom solution, it could cost even more. You should ask about these fees before you choose a gateway. They can affect your total costs a lot.
Software and hardware charges
POS systems have costs for both equipment and software. These fees can vary based on the features you need and the size of your business.
Point of sale (POS) equipment costs
POS hardware includes the physical devices you use to take payments. A basic setup often has a tablet, cash drawer, receipt printer, and card reader. Prices for these items range from $800 to $3000 or more.
Tablets can cost $200-$500 each. Cash drawers are usually $100-$200. Receipt printers range from $200-$400. Card readers can be $50-$200.
Some businesses need extra items. Barcode scanners cost $200-$400. Kitchen display systems for restaurants are $600-$1500.
Payment gateway software licenses
POS software lets you process sales and manage your business. Many companies charge a monthly fee for their software. These fees can be $0-$200 per month, depending on the features.
Basic plans often cost $50-$100 per month. They usually include sales tracking, inventory management, and customer data storage.
Advanced plans can be $150-$200 per month. These may add features like:
- Employee scheduling
- Loyalty programs
- Advanced reporting
Some companies offer free basic plans. But these often have limits on sales volume or number of users. Remember to factor in payment processing fees too. These are typically 2-3% of each sale, plus a small per-transaction fee.
10Web payments: Management and fees
If you’re hosting your ecommerce business website on 10Web, you can manage payments and fees effortlessly from one intuitive dashboard. 10Web Payments offers a unified solution that consolidates everything in one place, allowing you to manage transactions, review charges, and monitor payments without needing multiple third-party integrations.
10Web Payments is designed with transparent and straightforward fees, optimized specifically for online businesses. The platform charges a flat transaction fee of 2.9% + $0.30 per transaction, ensuring predictable costs with no hidden surprises. Unlike many other providers, 10Web Payments comes without setup fees or monthly subscription charges, helping you avoid unnecessary costs often associated with third-party processors.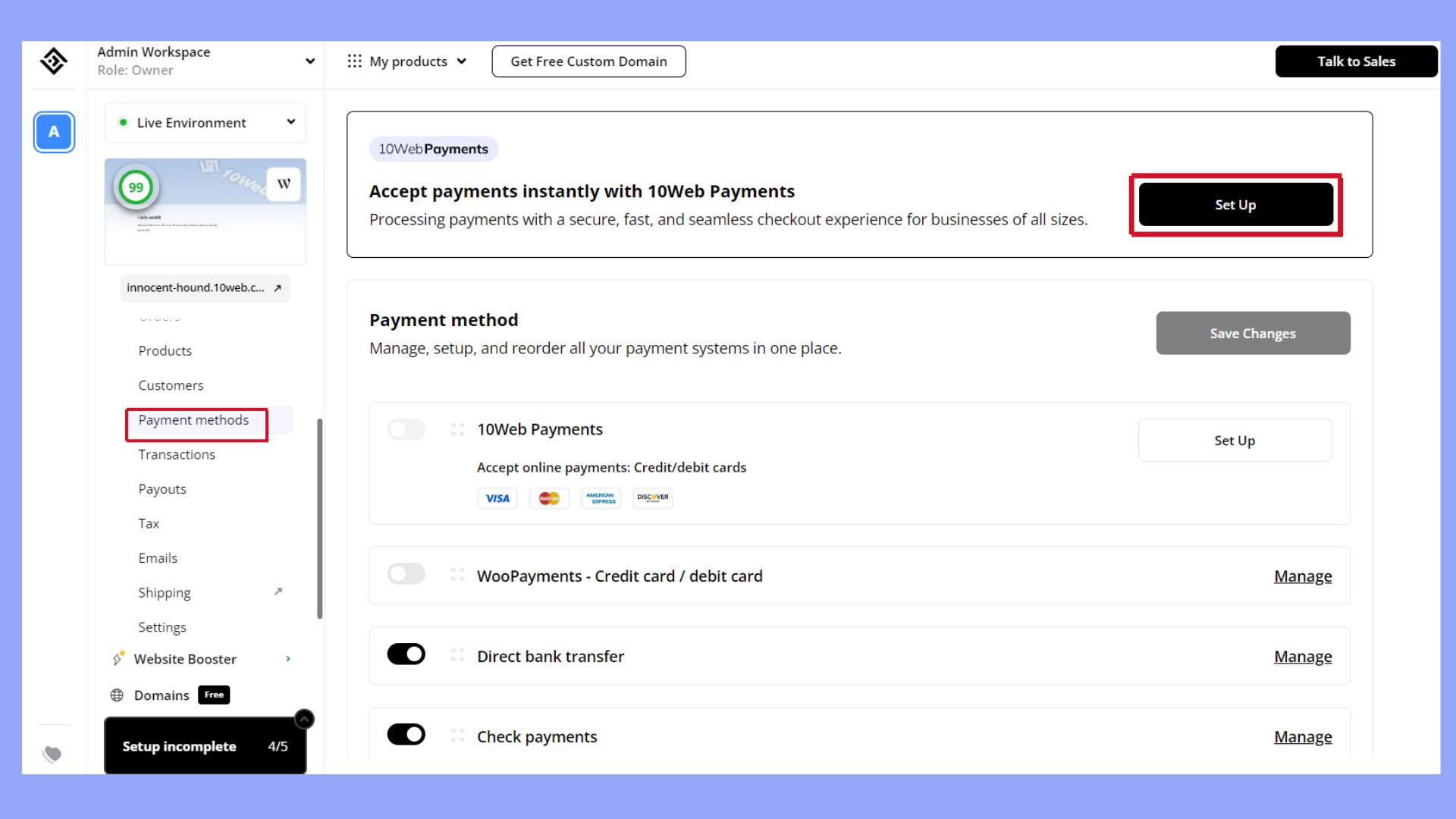
By centralizing your website hosting, payment management, and business analytics in the 10Web dashboard, you can keep operations seamless and efficient. This consolidation not only simplifies payment processing but also gives you a holistic view of your business’s financial health, making it easier to track profitability and make informed decisions.
Conclusion
When running an online store, if you want to manage cost effectively and maximize your profitability, you should learn the costs and fees involved. From transaction fees to international charges, understanding these fees helps you make informed decisions that support your business operations. By carefully selecting a payment gateway suited to your business model, transaction volume, and geographical market, you can effectively balance costs with convenience and security for your customers.
With platforms like 10Web Payments offering transparent, predictable pricing, ecommerce businesses now have solutions tailored to reduce unnecessary fees. Embracing such tools can simplify payment processing and provide better control over your financial planning, ultimately contributing to the long-term success and growth of your online business.
Looking to sell online? Develop and launch your store with 10Web AI Ecommerce Website Builder.
Create your online store in minutes!