There are two essential components for launching a website. Those are web hosting and the domain name. Though often confused, they have very distinct functions: a domain name is the address users type to find your site, while web hosting refers to the server where your site’s files are stored. Together, they make your website accessible online, but knowing the difference is crucial to building a reliable and effective online presence.
This article discusses the differences between domain names and web hosting, how they work together, and the factors to consider when choosing services. The growing demand for online businesses creates exciting opportunities to enhance branding through strategic domain selection and high-performance hosting, offering both flexibility and scalability to suit various website needs.
FAQ
Is web hosting the same as domain?
Is GoDaddy a domain or hosting?
Do I need web hosting for my domain?
Can I use hosting without a domain?
What is a domain name?
A domain name is like an address on the internet that helps people find a website. It consists of a name and an extension, such as “.com.” Understanding domain names is important because, without them, people would have to use complex strings of numbers known as IP addresses to access websites. Domain registration and DNS(Domain Name System) are key components in how a domain functions.
The role of domain names
Domain names serve as a website’s unique address, guiding users to its online location.
Instead of typing an IP address like “192.0.2.1,” users enter a memorable domain name such as “example.com.” This simplifies web navigation by making site addresses easier to remember.
Domains have several components: the top-level domain (TLD), like “.com,” and the second-level domain (SLD), which is the unique name part. The TLD follows the SLD after the dot. Examples of TLDs include generic TLDs (gTLDs) like “.org” and country-code TLDs (ccTLDs) like “.uk.”
How domain registration works
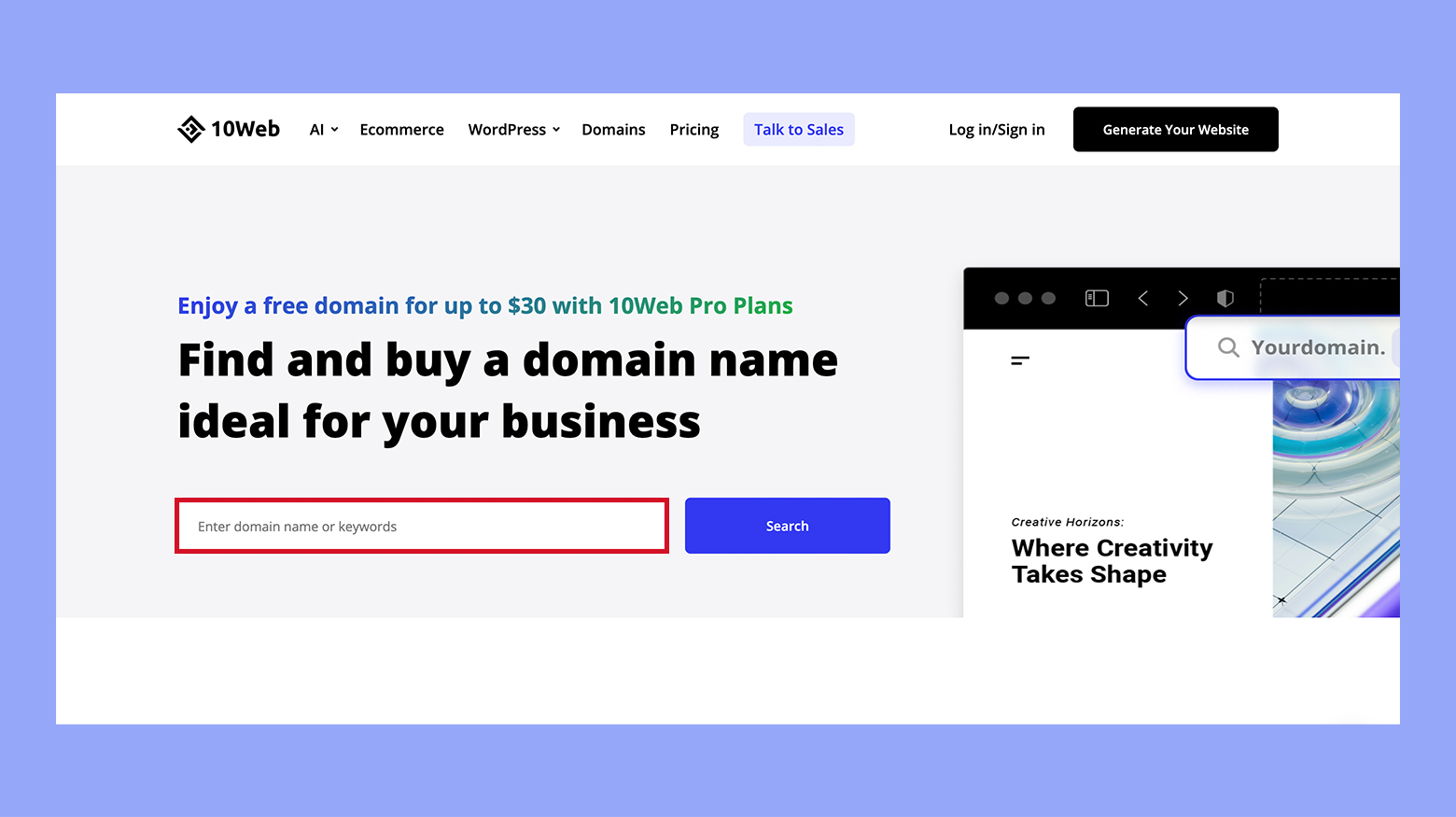
To utilize a domain name, it must be registered through a domain registrar.
On 10Web, the domain registration process is simplified for your convenience. Here is how it works:
- Access 10web.io/domain-name/
- Enter the desired domain name or a keyword and hit Search

- Once you select the domain, proceed to secure it by registering through 10Web
The platform provides options for domain privacy protection, helping to keep personal information private in the WHOIS database. It also offers domain management tools to handle renewals, DNS settings, and other important features, ensuring full control over the domain after registration.
The importance of DNS
The Domain Name System (DNS) is essential for translating domain names into IP addresses, making it possible for browsers to load websites. When a user enters a domain name, DNS servers find the associated IP address and direct the user to the correct site. DNS acts as a digital phonebook, ensuring that each domain name connects accurately to its hosting server.
It involves primary components like DNS records, which store important information about the domain. This system is crucial for website accessibility, as it handles queries from users worldwide, ensuring easy internet navigation. DNS is the backbone of internet communication, which enables efficient and reliable website access.
What is a web hosting?
Web hosting is a service that allows individuals and organizations to make their websites accessible on the internet. It involves storing website files on a server, so users can view them online. There are various types of web hosting services, each with unique features, to suit different needs.
Web hosting basics
Web hosting is an essential part of launching a website. At its core, web hosting involves storing website files on a server. When someone types your website name in a browser, the hosting server delivers the files, allowing the site to load.
Essential components are:
- Web host: The company providing the hosting service.
- Hosting server: Where files are stored and retrieved.
- Bandwidth: Controls the data flow between the server and users.
Web hosts often include tools to manage your site, such as a control panel. They also provide resources like disk space and an uptime guarantee, ensuring your website remains accessible.
Types of web hosting
Different hosting plans serve various website sizes and types. The most common types include:
- Shared hosting: Websites share server resources, making it cost-effective. It’s suitable for small sites.
- VPS hosting: Offers more dedicated resources compared to shared hosting. It’s ideal for growing businesses that need more control.
- Dedicated hosting: Provides exclusive server use, perfect for large websites needing enhanced performance.
- Cloud hosting: Distributes files across multiple servers, providing scalability and reliability.
Each type has its benefits and drawbacks, so choosing the right one depends on the specific needs of your business.
Choosing a web hosting provider
When selecting a web hosting company, consider important factors like those.
- Uptime guarantees: Ensure the provider offers reliable uptime (99.9% or higher) to minimize downtime.
- Customer support: 24/7 support is essential, especially if you’re not experienced with technical troubleshooting.
- Pricing: Compare plans and see what’s included, ensuring there’s a good balance between cost and features.
- Performance and speed: Look for fast loading times and a Content Delivery Network (CDN) for global optimization.
- Scalability: Ensure the provider offers scalable hosting to accommodate future growth.
- Security features: Check for SSL certificates, malware protection, and firewalls.
- Data center locations: Choose a provider with data centers close to your target audience for better performance.
- Backup: Regular automated backups and easy data recovery are important for data safety.
10Web provides managed WordPress hosting with features such as automated website optimization, AI-driven website creation, and strong backup and security systems. Managed hosting is ideal if technical tasks aren’t your forte, as it handles complex aspects of server management for you.
Try 10Web for free, and enjoy all the benefits of a secure Google Cloud Partner hosting and 10Web's AI Website Builder.![]()
#1 Managed WordPress Hosting
Differentiating domain and hosting
Domains and hosting are different yet both are important for running a website. A domain acts like the website’s address, while hosting serves as the space where the website’s data is stored.
Connection between domain and hosting
A domain and hosting work together, allowing users to access a website. The domain, like example.com, directs a user to the website. When someone types the domain into a browser, the browser uses the domain to find the host’s server where the website data is stored.
Without a domain, it would be challenging for users to find a website. Similarly, without hosting, there would be no files to display when someone visits the domain. They work in harmony to ensure a website is accessible and lives online.
Impact on website identity and access
A domain name significantly impacts a website’s identity. It is part of the branding, creating a recognizable online presence. A good domain name should be easy to remember and reflect the purpose of the website.
Hosting affects how a site is accessed based on speed and uptime. Good hosting ensures that a website is available when users need it. Users’ experience with the site can be influenced by the reliability and speed of the host, contributing to the site’s credibility.
This connection is established using DNS settings. The domain’s settings point to the hosting server, telling internet browsers where to fetch the website’s files. Proper coordination between these services ensures that visitors can freely access the website online.
Impact of hosting on website performance
Website hosting plays a key role in shaping how well a site performs. Two main factors are critical: the speed and uptime of the server, and the resources provided by the server. Understanding these can help you make better hosting decisions.
Assess server speed and uptime
Server speed has a direct effect on how quickly your website loads. Fast servers help websites load in seconds, improving user experience. Quick loading times not only keep visitors happy but can also boost search engine rankings. Uptime, on the other hand, means how often the server is working without issues. A server with good uptime is always available when users want to visit your website.
Web hosts often promise 99.9% uptime—but it’s important to verify this claim. Frequent downtimes can annoy users and harm your site’s reputation. So, checking both speed and uptime is essential when looking at hosting options.
Server resources and website efficiency
The available resources from a server can determine how smoothly your website functions. These resources include RAM, CPU, and storage. With more RAM and CPU power, your website can handle more traffic without slowing down.
Shared hosting may limit server resources since you’re sharing them with other websites. This can affect page load times and overall site efficiency. Conversely, dedicated hosting provides full server resources just for you, which can optimize website performance. It’s vital to match your site’s needs with the server resources to maintain a balance between cost and performance.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between web hosting and domain names is fundamental to building a successful website. While a domain name provides a memorable address for users to locate your site, web hosting ensures that the site’s files are stored and accessible online.
Both are essential components, working together to deliver a seamless experience for users. By selecting the right domain and hosting service, businesses can improve their online presence, site performance, and ensure reliability. Whether you’re just starting or looking to scale, making informed choices about your domain and hosting can set the foundation for long-term success online.
Try 10Web for free, and enjoy all the benefits of a secure Google Cloud Partner hosting and 10Web's AI Website Builder.![]()
#1 Managed WordPress Hosting